Comparative advertising is a marketing tactic which helps to drive brand awareness by comparing their product or service to a competitor.
When executed correctly, comparative ads can successfully convince consumers to do business with one brand over another. But, this strategy requires care and attention, especially as companies may find themselves in the middle of a lawsuit.
In this post, we’ll delve deeper what comparative advertising is, give real-life business examples, explain the legality of using the strategy, and present pros and cons that you can use to make the best decision for your business.
half of US adult internet users stating that advertising helps them to discover and find products or services that interest them, getting your brand messaging right is crucial. Through messaging, like comparative advertising, you can communicate the value of your product or service to your audience.
1960s and ’70s, companies have used comparative ads to directly or indirectly mention a competitor. Comparative ads give customers a direct point of comparison between two companies, as they can view products and assess features all at once, rather than needing to seek out information from multiple sources.
4.65 billion people now actively use social media.
Why Is Comparative Advertising Effective (Comparative Advertising Examples)
Popeyes
Why this example works:
Sprint
Why this example works:
Cocoon by Sealy
Why this example works:
increases brand awareness by up to 80%.

Adidas
Why this example works:
Kroger
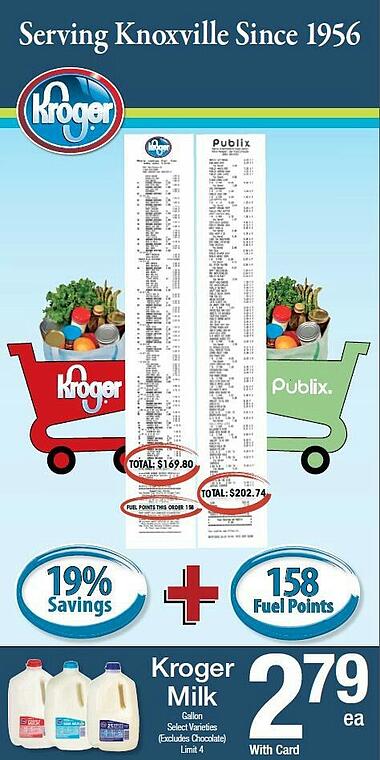
Why this example works:
82% of consumers trust print advertising, making it an effective way to enhance the brand’s credibility.
Bounty

Why this example works:
Comparative Advertising Law
United States Comparative Advertising Law
ruled on comparative advertising and said, “Comparative advertising, when truthful and nondeceptive, is a source of important information to consumers and assists them in making rational purchase decisions. Comparative advertising encourages product improvement and innovation, and can lead to lower prices in the marketplace.”
Australia Comparative Advertising Law
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission says that “Businesses may use comparative advertising to directly promote the superiority of their products over another.” Like U.S. law, businesses must follow general advertising best-practices of not being deceptive or misleading in an attempt to entice consumers to do business with them.
Hong Kong Comparative Advertising Law
prohibits false trade descriptions and misleading or incomplete information advertisements, and the Association of Accredited Advertising Agencies of Hong Kong
has the authority to investigate instances of violation.
Comparative Advertising Pros and Cons
Pros
Explicit product emphasis.
You’ll raise awareness of your business.
You’ll gain new followers and attract new clients.
208 million people tuned in.
You’ll teach consumers about what is important.
As comparative ads focus on a specific feature or experience that comes with a product or service, you’re informing consumers about the factors they should keep in mind when making purchasing decisions.
Cons
You may lose integrity and look bad to your audience.
40% of marketers do – yet it’s a crucial aspect in producing successful advertisements.
It can create brand name confusion.
You can face legal action.
As mentioned above, many countries have laws protecting consumers and other businesses from comparative ads.
You need to produce your ad with the utmost care and attention, otherwise, you may face legal action from your competitors. If you’re a big name brand, publications will likely report on it, which can also negatively impact your reputation.
Comparative Advertising Can Help Your Business Grow
market share and position yourself as an industry leader.
![what-is-comparative-advertising?-[+-examples]](https://prodsens.live/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/4427-what-is-comparative-advertising-examples-550x299.png-23keepprotocol)






