Applying the right project management best practices can make the difference between failure and success. These proven techniques help ensure that projects stay on track, within scope and on budget. Whether you’re a seasoned manager or just getting started, understanding and implementing these practices will boost your project outcomes. From goal setting to risk management, this guide will walk you through essential steps to keep your team focused and your stakeholders satisfied.
1. Begin by Setting Project Goals and Objectives In a Project Charter
A project charter is a foundational document that outlines the purpose, scope and key stakeholders of a project. It authorizes the project, names the project manager and defines the initial project requirements to satisfy stakeholder expectations. Typically created in the initiation phase, this document helps align the team and stakeholders by providing a clear direction. It also serves as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle to measure progress and ensure accountability.
Project goals are broad, long-term outcomes that the project aims to achieve. Objectives, on the other hand, are specific, measurable actions that lead to the completion of those goals. By defining both clearly in the project charter, teams ensure alignment, reduce ambiguity and create a roadmap that links daily tasks to the overall vision.
Setting clear goals and objectives provides direction and purpose when using ProjectManager software, helping teams align their work with broader manufacturing or business priorities. With defined goals in place, users can break down objectives into actionable tasks, assign responsibilities and track progress in real time using our planning tools.
Features like Gantt charts link dependencies to avoid costly delays, filter for the critical path to identify tasks with zero slack and set a baseline to track progress in real time. Some dashboards and reports allow teams to monitor performance against these goals, make data-driven adjustments and stay focused on outcomes. This alignment ensures resources are used effectively and projects stay on track from start to finish. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
2. Create a Business Case to Justify the Project
A business case outlines the reasons for undertaking a project, analyzing its benefits, risks and costs. It’s a strategic tool used to pitch the project to stakeholders, ensuring there’s a strong justification for investment. Without a solid business case, projects can lack direction or stakeholder support. This document helps decision-makers understand how the project aligns with organizational goals and what return on investment they can expect, ultimately improving the chances of approval and success.
3. Make a Thorough Project Plan
A project plan is the central document that defines how the project will be executed, monitored and closed. It encompasses all aspects of project management, including scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, communication, risk and procurement. Without this plan, teams may lose direction or miscommunicate priorities. It ensures that every project management knowledge area is accounted for and handled effectively.
The plan serves as a living document, guiding decision-making and coordination across departments while ensuring that deliverables align with stakeholder expectations. By documenting processes, dependencies and key milestones, the project plan helps minimize surprises and fosters accountability. It also offers a structured approach to adapt and respond to changes, giving project managers better control. Ultimately, a thorough project plan sets the foundation for a predictable and successful project outcome.
4. Establish a Project Baseline for Better Project Control
A project baseline includes the original scope, schedule and budget. It serves as a benchmark to compare actual progress and performance against what was initially planned. Without this reference point, teams wouldn’t have a clear target to manage against. Establishing a baseline allows project managers to detect variances early, make informed decisions and keep stakeholders aligned. It’s a crucial control tool that provides visibility and keeps the project from drifting off course.
Related: Best Project Management Software of 2025
5. Make a Work Breakdown Structure to Define Project Scope
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work in a project. It breaks down the project into smaller, more manageable components, starting with high-level deliverables and dividing them into work packages or tasks. The WBS visually organizes work to clarify what needs to be delivered and ensures no part of the scope is overlooked.
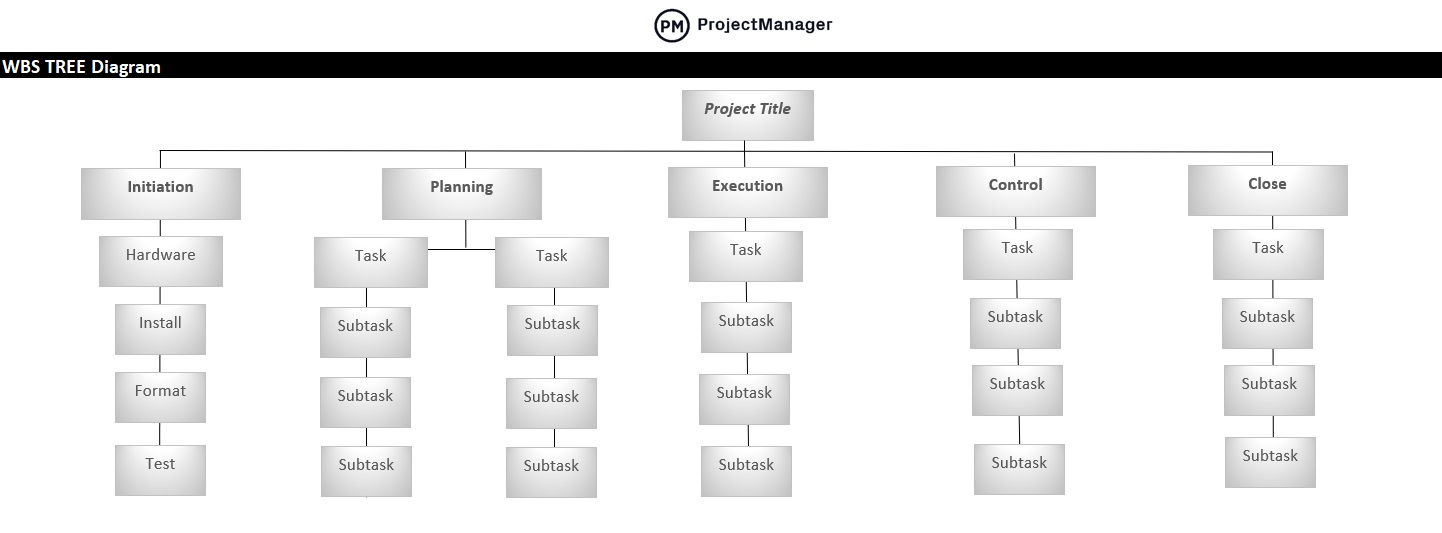
The WBS is essential for project planning because it defines the project work on a task level. This level of detail makes it easier to create the project schedule, allocate resources effectively and estimate costs accurately. By organizing work in a structured format, the WBS supports communication among stakeholders and promotes accountability. It also helps avoid scope creep by clearly outlining what’s included—and what’s not—in the project’s scope.
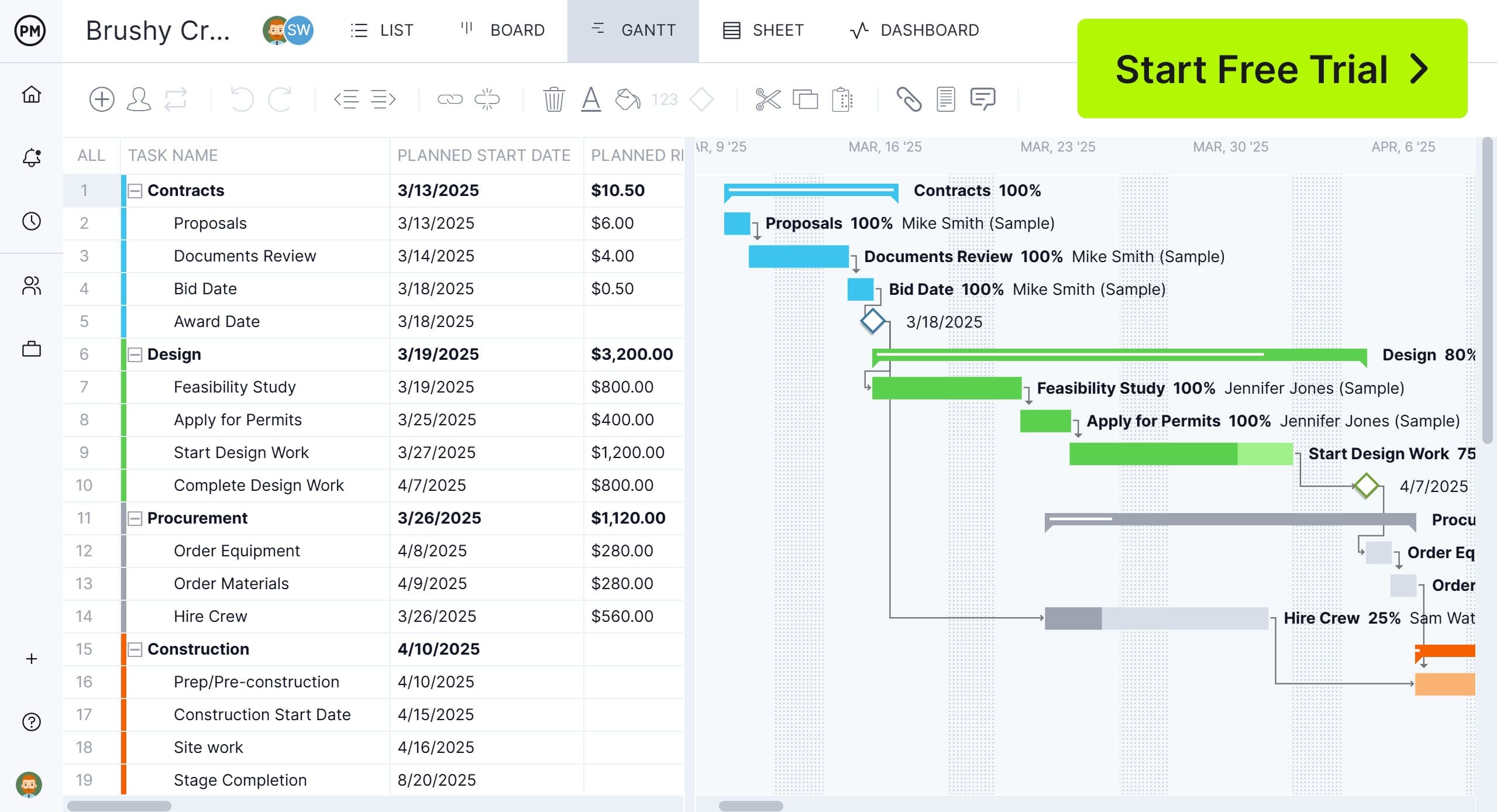
6. Use a Gantt Chart to Visualize the Project Schedule
A Gantt chart is a visual project scheduling tool that displays tasks over time. It consists of two main elements: a grid that lists tasks, durations and assigned resources, and a horizontal stacked bar chart aligned to a calendar timeline. Each bar represents a task’s duration and placement along the timeline, showing start and end dates. Dependencies between tasks can also be mapped with connecting lines.
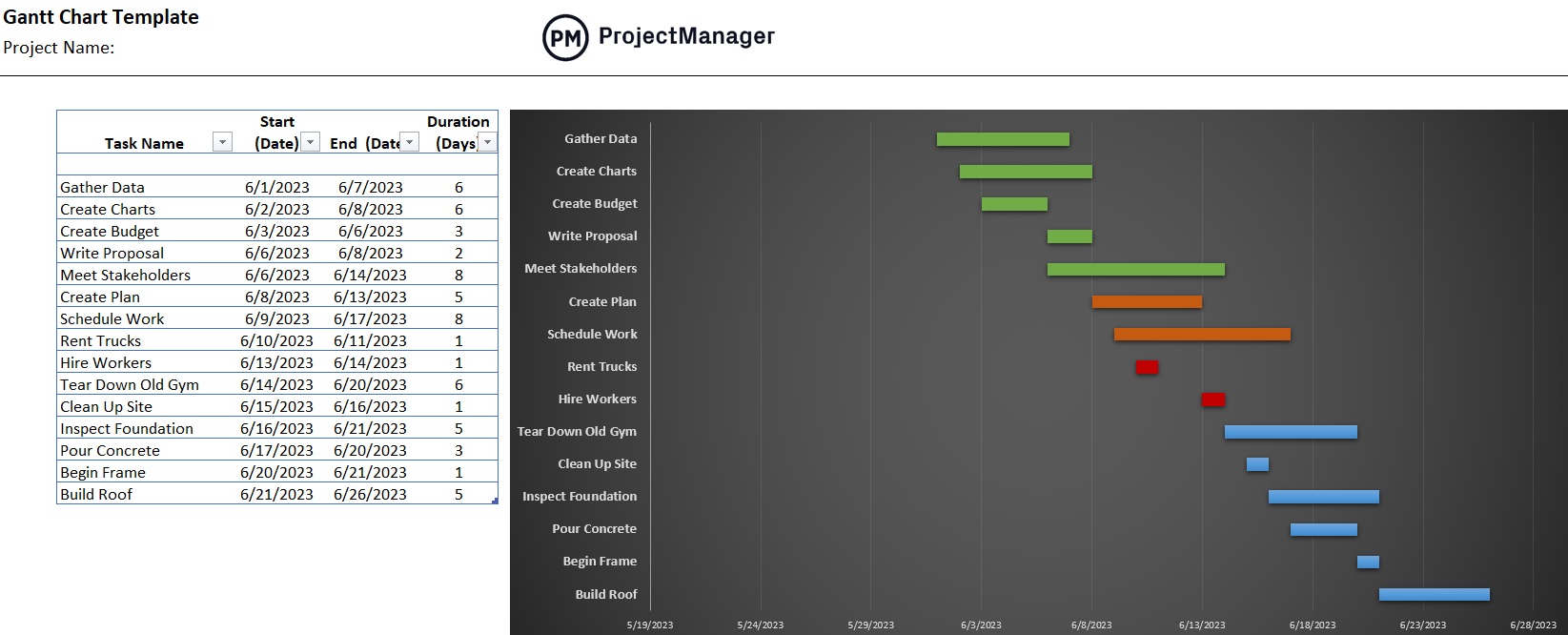
Gantt charts are among the most versatile project management tools because they provide a clear overview of the project timeline. Managers can identify task dependencies, track progress in real time and adjust plans as needed. They’re useful not only for scheduling but also for monitoring and controlling project execution. By making timeframes, responsibilities and status visible, Gantt charts help ensure everyone stays on the same page throughout the project lifecycle.
7. Use the Critical Path Method to Prioritize Project Tasks
The critical path is the longest sequence of dependent tasks in a project that determines the shortest possible completion time. If any task on this path is delayed, the entire project is delayed. The critical path highlights which activities are critical and which have scheduling flexibility, making it a key concept in time management.
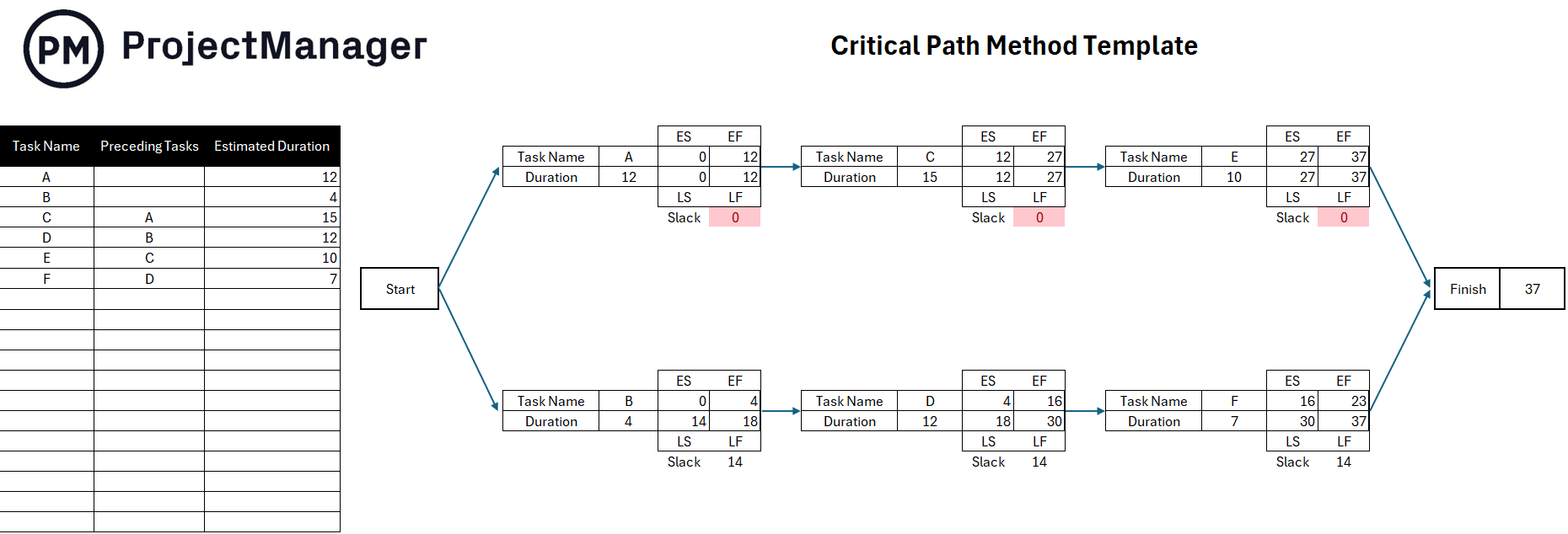
Identifying the critical path activities helps project managers prioritize where to focus efforts and allocate resources. These tasks must be completed on time to keep the project on schedule. Knowing which tasks are critical allows managers to make better decisions during scheduling and execution. It also helps avoid wasting time on activities with slack, enabling the team to concentrate on the tasks that truly determine the project’s success.
8. Avoid Scope Creep Throughout the Project Execution Phase
Scope creep refers to the uncontrolled expansion of a project’s scope without adjustments to time, cost or resources. It often occurs when new tasks or deliverables are added without formal approval. Scope creep can lead to missed deadlines, budget overruns and overworked teams. It’s one of the most common threats to successful project delivery, especially in long or complex projects.
To avoid scope creep, first establish a change control procedure. This means that any new requests must go through a formal process to assess their impact before being approved. Second, define the scope clearly in the project plan and communicate it with all stakeholders to prevent misunderstandings. Third, maintain regular check-ins and progress reviews. These meetings help identify unauthorized changes early and provide opportunities to reinforce the agreed-upon scope.
9. Establish an Acceptance Criteria of Project Deliverables
Establishing clear and detailed acceptance criteria for project deliverables ensures that all work meets predefined standards before it’s considered complete. These criteria outline measurable conditions such as quality, functionality and performance, which help reduce misunderstandings between stakeholders and project teams. It also supports quality control, aligns expectations and provides a framework for review and approval. Without acceptance criteria, teams may deliver incomplete or unsatisfactory results, leading to delays, rework and dissatisfaction from clients or sponsors.
10. Evaluate Project Constraints Early in the Project Life Cycle
Project constraints include time, cost, scope, quality, resources and risk. These limitations shape how a project is planned and executed. Evaluating constraints early in the project life cycle—particularly during initiation and planning—is essential for setting realistic goals. It ensures that expectations are managed and trade-offs are understood. Factoring in constraints early helps prevent future conflicts, supports decision-making and improves the chances of delivering a successful project on time, on budget and according to stakeholder expectations.
11. Compare Estimated vs. Actual Costs to Stay Within the Project Budget
Estimating project costs is only the first step in managing a project budget. Once the project is underway, actual costs must be tracked continuously and compared to the original estimates.
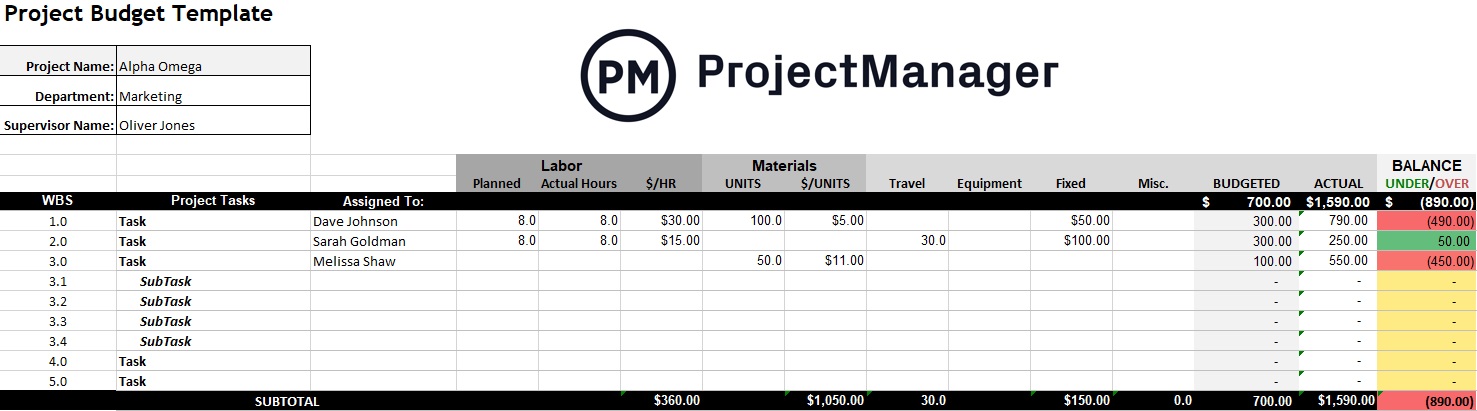
This ongoing comparison allows the project manager to identify variances early, understand their causes and take corrective action before the budget is exceeded. It also supports more accurate forecasting and accountability. By closely monitoring costs, managers can make better financial decisions, stay aligned with stakeholders and ensure that resources are used efficiently.
12. Familiarize Yourself with Project Management Methodologies
Project managers should be well-versed in a variety of project management methodologies, such as Waterfall, Agile, Scrum or Hybrid. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses and is suited for different types of projects. By understanding these approaches, a project manager becomes more adaptable and can select the methodology that best fits the project’s complexity, size, timeline or stakeholder requirements. This versatility enhances the manager’s ability to respond to challenges, improve team collaboration and ensure successful outcomes across a wide range of project environments.
13. Establish a Risk Management Plan
Every project carries risk. That’s why it’s essential to create a risk management plan that identifies potential threats, assesses their likelihood and impact, and defines mitigation strategies. Establishing this plan early helps minimize disruption during execution and supports proactive decision-making. Without a risk management plan, teams are left reacting to issues instead of preparing for them. A documented process for monitoring and addressing risks improves resilience and gives stakeholders confidence that the project will remain on track even in the face of uncertainty.
14. Ensure Project Stakeholders Have Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic stakeholder expectations from the beginning ensures alignment throughout the project. When expectations are clearly defined during the initiation phase, stakeholders are less likely to request major scope changes or feel disappointed later. Unrealistic expectations can lead to dissatisfaction, strained relationships and failure to meet perceived project goals. Managing these expectations early supports smoother execution, better communication and long-term stakeholder satisfaction.
15. Use Project Management Software
Project management software centralizes all project information, helping teams plan, schedule and track their work more efficiently. These tools offer features such as task assignments, time tracking, Gantt charts and real-time collaboration.
By providing visibility into progress and resource usage, the software supports informed decision-making and helps keep the project on schedule and within budget. It also improves communication among stakeholders and reduces the risk of misalignment by ensuring everyone has access to the most up-to-date information.
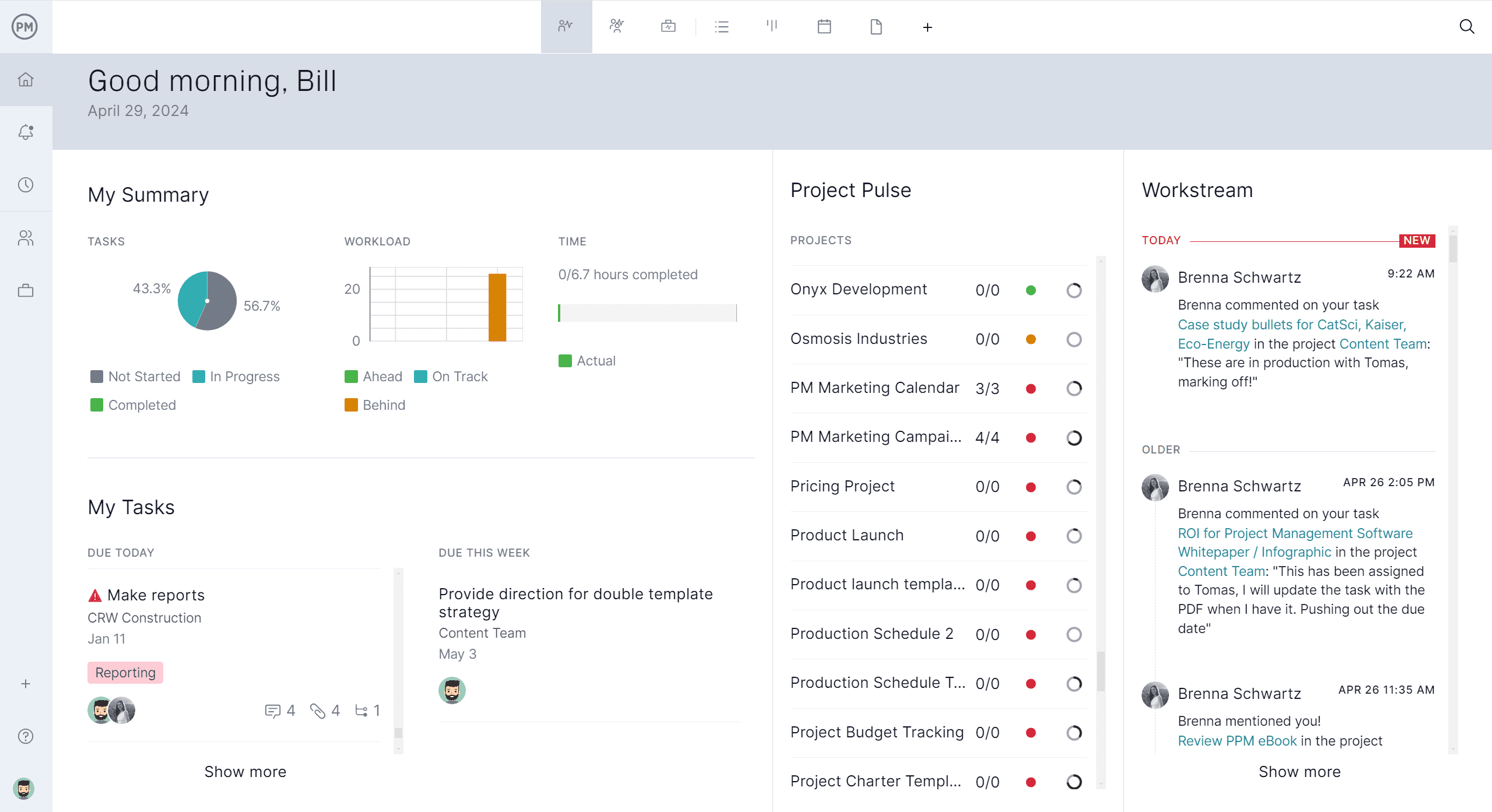
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Projects
When you choose project management software, make sure you choose the right one. ProjectManager helps manage projects by using resource management tools like availability settings, workload charts and the team page to give managers clear visibility into team capacity and task distribution. Availability settings account for each team member’s working hours and time off, allowing for more accurate scheduling. Workload charts show real-time task assignments to highlight who is over- or under-allocated so adjustments can be made quickly. The team page centralizes this data, making it easy to view roles, responsibilities and workloads at a glance to keep projects balanced and on track.
Let Teams Work How They Want to
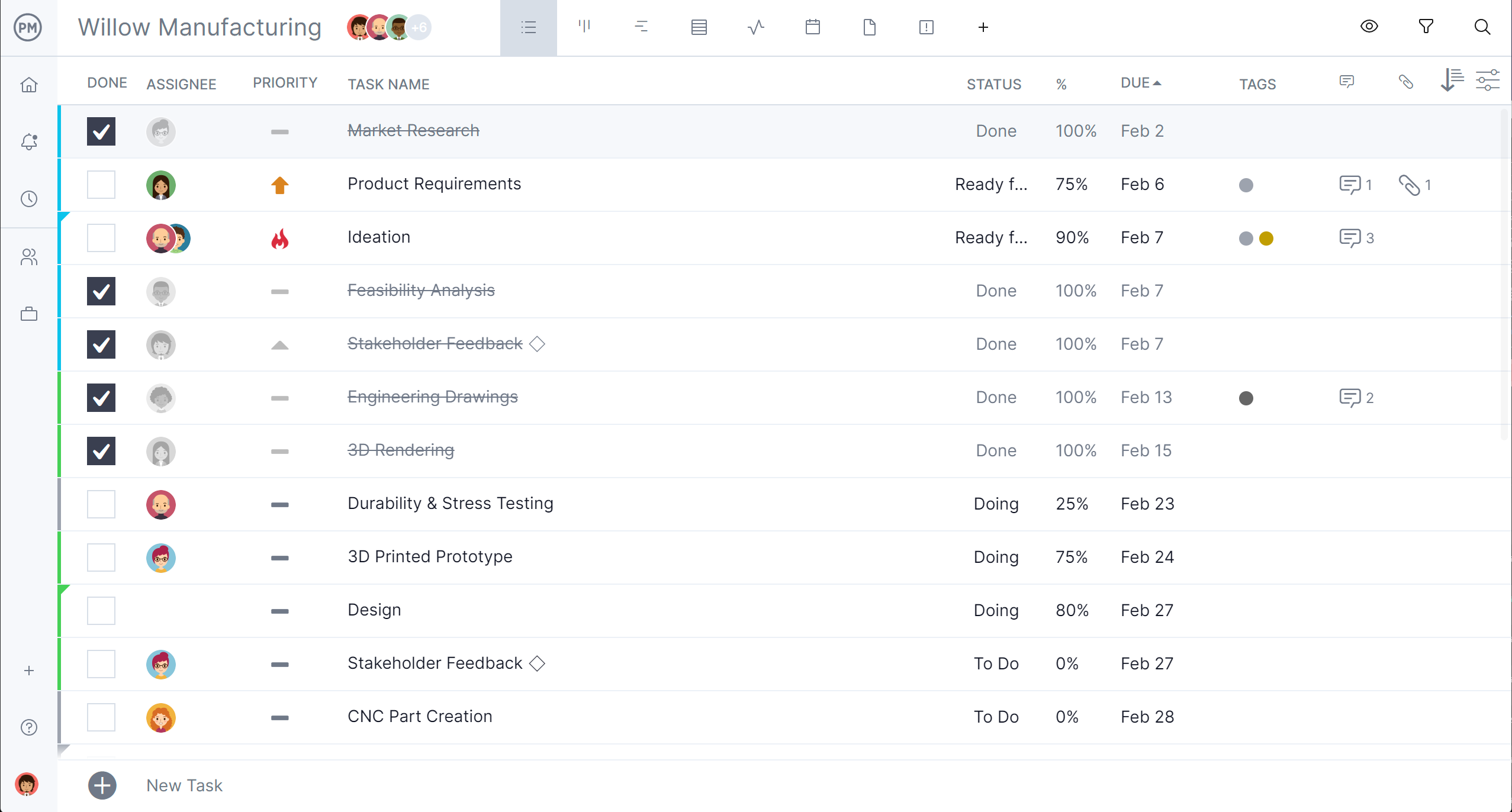
Use multiple project views—including Gantt chart, kanban board, calendar, sheet and list view—to help teams manage work according to their preferred style or workflow. The list view is especially useful for managing projects because it provides a structured, task-by-task breakdown with key details like due dates, assignees and priority levels all in one place.
This makes it easy to sort, filter and update tasks while keeping everything organized and visible. Whether used for simple to-do lists or complex production schedules, the list view supports clarity and control, helping teams stay focused and on track.
Track Work in Real Time
Tracking features help teams stay on top of every aspect of a project by delivering real-time updates and visibility into task progress, resource usage and deadlines. With tools like live dashboards, customizable reports and secure timesheets, managers can monitor performance as work happens, spot delays or bottlenecks and make informed adjustments about labor costs quickly.
Task status updates, time tracking and progress bars ensure accountability while keeping everyone aligned with project goals. This constant insight improves efficiency, supports better decision-making and keeps projects moving forward on schedule.
Related Project Management Content
While project management best practices are a good place to start, there is much more to learn about project management. For those interested in expanding their knowledge, follow the links below. They lead to articles on tools, techniques and much more.
- 22 Project Management Tools & Techniques for Project Managers
- 40 Project Management Skills: Soft, Hard & Technical Skills
- 21 Best Project Management Certifications (2025)
- The 5 Project Management Phases: A Quick Guide
- The 10 Project Management Knowledge Areas – (PMBOK)
- 100+ Project Management Terms: PM Terminology
- 14 Key Project Management Principles & How to Use Them
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
The post 15 Project Management Best Practices for Successful Projects appeared first on ProjectManager.