Learning how to write a proposal is a valuable skill, whether you’re pitching a business idea, seeking funding or suggesting a new work project. A good proposal starts with a clear introduction that explains what you’re proposing and why it matters. Keep your language straightforward and focused and adjust your message to suit your audience. Aim to present your idea in a way that highlights its relevance and potential impact without overwhelming the reader with unnecessary details.
The main body should support your idea with essential information like expected outcomes, resources and a simple timeline. Use bullet points or headings if they help make your points easier to follow, and end with a clear call to action or next step to encourage a response.
What Is a Proposal?
A proposal is a structured document that presents an idea, solution or plan to stakeholders to gain approval or secure funding. It outlines objectives, methods, timelines and expected outcomes while making the case for why the proposed approach is the best option. Learning how to write a proposal means understanding both the audience and the problem that needs to be solved so that the document communicates value clearly and persuasively.
Proposals can take many forms depending on the context, such as business, academic or nonprofit projects. Regardless of type, they typically include an introduction, problem statement, proposed solution, methodology, costs and benefits. Mastering how to write a proposal ensures that every section flows logically and supports the central argument, giving decision makers the confidence to move forward with the plan.
Project management software is the best tool for supporting this process because it streamlines planning, organizing and tracking the details that go into proposal development. It helps teams collaborate in real time, centralize resources, manage deadlines and ensure that no part of the proposal is overlooked. With visual timelines and task management tools, software reduces complexity and increases efficiency, leading to a polished and professional proposal.
ProjectManager is the best choice for creating and managing proposals because it combines ease of use with powerful planning tools. Its Gantt charts are especially valuable for mapping proposal timelines, assigning responsibilities and tracking progress against milestones. In addition, ProjectManager offers multiple project views, robust collaboration features and real-time reporting, giving teams everything they need to create winning proposals and execute them successfully once approved. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Common Types of Proposals
When learning how to write a proposal, it’s important to understand that they come in different forms depending on the context. Each type serves a specific purpose and has unique elements that must be included to meet the audience’s needs. Below are some of the most common types of proposals, each requiring a slightly different approach but all benefiting from clear structure and strong communication.
Project Proposal
A project proposal outlines the scope, objectives and strategy for completing a project. It explains the problem being addressed, the solution being proposed and the timeline for execution. Knowing how to write a proposal of this kind requires breaking down tasks into manageable steps and showing stakeholders how resources will be used. The goal is to convince decision makers that the project is realistic, achievable and aligned with organizational goals.

Get your free
Project Proposal Template
Use this free Project Proposal Template to manage your projects better.
Business Proposal
A business proposal is designed to persuade potential clients or partners to work with a company. It typically includes an introduction to the company, the services or products being offered, pricing and the benefits of choosing that business.
Learning how to write a proposal in this format involves tailoring the content to the client’s needs and demonstrating clear value. A strong business proposal highlights competitive advantages and builds trust with the audience.
Work Proposal
A work proposal is often used to outline tasks, responsibilities and deliverables for a job or contract. It clearly defines what will be done, how it will be done and the timeframe for completion. Understanding how to write a proposal like this is crucial for freelancers, contractors or employees who need to gain approval before starting work. Setting clear expectations helps both parties avoid misunderstandings and ensures accountability.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is a formal request for funding from a government agency, foundation or nonprofit organization. It typically includes background information, objectives, a detailed plan of action and a budget. Mastering how to write a proposal in this style requires attention to detail and alignment with the funder’s priorities. A successful grant proposal demonstrates both the significance of the project and the ability of the applicant to deliver measurable results.
Event Proposal
An event proposal is used to present the plan for hosting a conference, meeting or special occasion. It outlines the purpose of the event, the target audience, logistics, budget and expected outcomes. Knowing how to write a proposal for an event means showing how the event will meet goals and provide value to participants. A strong event proposal highlights organization, creativity and the ability to manage resources effectively to ensure success.
How to Write a Project Proposal
When learning how to write a proposal for a project, it’s essential to follow a structured format that covers every critical aspect. A well-prepared project proposal not only communicates the value of the initiative but also provides clarity for stakeholders. Below are the key sections that should be included when writing a project proposal, each with a clear purpose in helping secure approval and ensuring a successful outcome.
1. Project Background or History
This section provides context by explaining the background or history of the project. It shows why the project is being proposed and what has led to its consideration. Understanding how to write a proposal with a strong background builds credibility and sets the stage for the rest of the document. Including relevant history demonstrates awareness of past challenges and positions the new project as a well-informed initiative.
2. Business Problem and/or Business Opportunity
Identifying the problem or opportunity is a critical step when deciding how to write a proposal. This section outlines the pain points or market gaps that the project aims to address. Framing the issue in concrete terms helps stakeholders understand the urgency and importance of moving forward. A compelling problem statement makes the proposal more persuasive and strengthens the case for the proposed solution.
3. Proposed Solution
The proposed solution explains how the project will address the identified problem or opportunity. Knowing how to write a proposal in this section means providing a clear and actionable plan that shows feasibility and alignment with organizational goals. It should describe the approach, methods and tools that will be used. A strong solution gives decision makers confidence that the project can achieve its intended outcomes.
4. Project Vision and Goals
Defining the vision and goals sets the direction for the project and provides measurable objectives. When learning how to write a proposal, this section should highlight both the long-term vision and the short-term goals. It ensures that all stakeholders share a common understanding of what success looks like. Well-articulated goals also make it easier to evaluate progress and maintain alignment throughout the project.
Related: 10 Free Goal-Setting and Tracking Templates for Excel and Word
5. Project Deliverables
Deliverables are the tangible outputs that the project will produce. In learning how to write a proposal, it’s essential to list these items so stakeholders know what to expect. This may include reports, products, services or systems that will be delivered. By outlining deliverables, the proposal establishes accountability and provides benchmarks that can be used to measure project completion and success.
6. Project Timeline (or Timeframe)
The timeline provides a schedule for when tasks and milestones will be completed. Knowing how to write a proposal with a clear timeline helps set realistic expectations and ensures proper planning. It should include start and end dates, key milestones and any dependencies between tasks. A well-structured timeline shows that the project has been carefully thought out and can be executed efficiently.
7. Resource Requirements
This section details the resources needed to complete the project, such as personnel, equipment and materials. Understanding how to write a proposal with resource requirements ensures that decision makers can assess feasibility and allocate support. It also demonstrates that the project team has considered what is necessary for success. Identifying resources reduces the risk of delays and cost overruns later on.
8. Estimated Project Budget
The budget outlines the financial requirements for the project. Learning how to write a proposal in this section involves estimating costs for labor, materials, tools and other expenses. Providing a detailed budget helps stakeholders evaluate affordability and return on investment. A transparent and realistic budget strengthens the proposal by showing that financial planning has been carefully considered and accounted for.
9. Potential Project Risks
Identifying risks is an important part of learning how to write a proposal. This section outlines possible challenges or obstacles that could impact the project. By acknowledging risks and providing mitigation strategies, the proposal shows foresight and preparedness. Stakeholders are more likely to support a project that anticipates potential setbacks and has a plan to manage them effectively.
10. Project Success Criteria
Success criteria define how the project’s outcomes will be measured and evaluated. When learning how to write a proposal, this section should include clear metrics such as quality standards, completion dates or performance indicators. Establishing success criteria gives stakeholders confidence that the project will be tracked and assessed objectively. It also provides the team with a framework for achieving and demonstrating success.
Project Proposal Template
Download this free project proposal template to organize and present the key details of a project idea clearly and professionally. It guides users through essential sections such as background, goals, deliverables, timeline and budget so they can focus on content instead of structure.
Using a project proposal template streamlines the process, saves time and ensures consistency, making it easier to learn how to write a proposal that secures stakeholder approval.
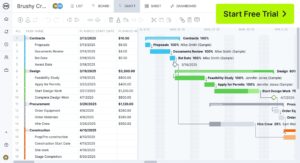
Project Proposal Example
To better understand how a project proposal works, below is an example of a company implementing a unified, digital self-service experience.
The proposal shows how standardized workflows will reduce manual labor, accelerate resolution and unlock actionable analytics
How to Write a Business Proposal
When learning how to write a proposal for business opportunities, it’s important to create a clear and persuasive document that addresses the client’s needs. A well-structured business proposal demonstrates understanding of the problem, offers a practical solution and establishes credibility. The following sections outline the essential components of a business proposal, helping you present ideas effectively and increase the chance of winning new clients or partnerships.
1. Problem Statement
The problem statement defines the challenge your client is facing. Knowing how to write a proposal means clearly outlining this issue to show you understand their situation. A concise problem statement sets the stage for presenting your solution and builds trust by demonstrating empathy and awareness.
2. Needs Analysis
A needs analysis identifies the client’s requirements and priorities. When learning how to write a proposal, this section highlights what the client values most, whether it is cost savings, efficiency or innovation. Addressing these needs directly ensures your proposal aligns with the client’s goals and expectations.
3. Proposed Solution
The proposed solution explains how your product or service will solve the client’s problem. Understanding how to write a proposal in this section involves being specific and results-oriented. A strong solution not only addresses the problem but also highlights the benefits that make your offer stand out from competitors.
4. Project Scope
The project scope defines what will and will not be included in your services. Learning how to write a proposal with a clear scope prevents misunderstandings and sets realistic expectations. By outlining boundaries, you create accountability and provide a framework for successful project delivery.
5. Project Timeline
The timeline shows how long the project will take and when key milestones will be met. When learning how to write a proposal, this section reassures clients that you can deliver on schedule. A detailed timeline builds confidence in your planning and execution capabilities.
6. Estimated Cost Breakdown
This section presents a transparent cost structure for the project. Understanding how to write a proposal here means breaking down expenses so clients see exactly what they are paying for. A clear and honest budget fosters trust and demonstrates financial responsibility.
7. Company Overview
The company overview introduces your business and explains why you are the right choice. Learning how to write a proposal with this section involves highlighting your experience, expertise and past successes. It helps establish credibility and reassures clients that you can deliver results.
8. Terms and Conditions
The terms and conditions define the rules of engagement, including payment terms, responsibilities and legal considerations. Knowing how to write a proposal with well-defined terms ensures both parties are protected. It provides clarity and prevents disputes, laying the groundwork for a smooth working relationship.
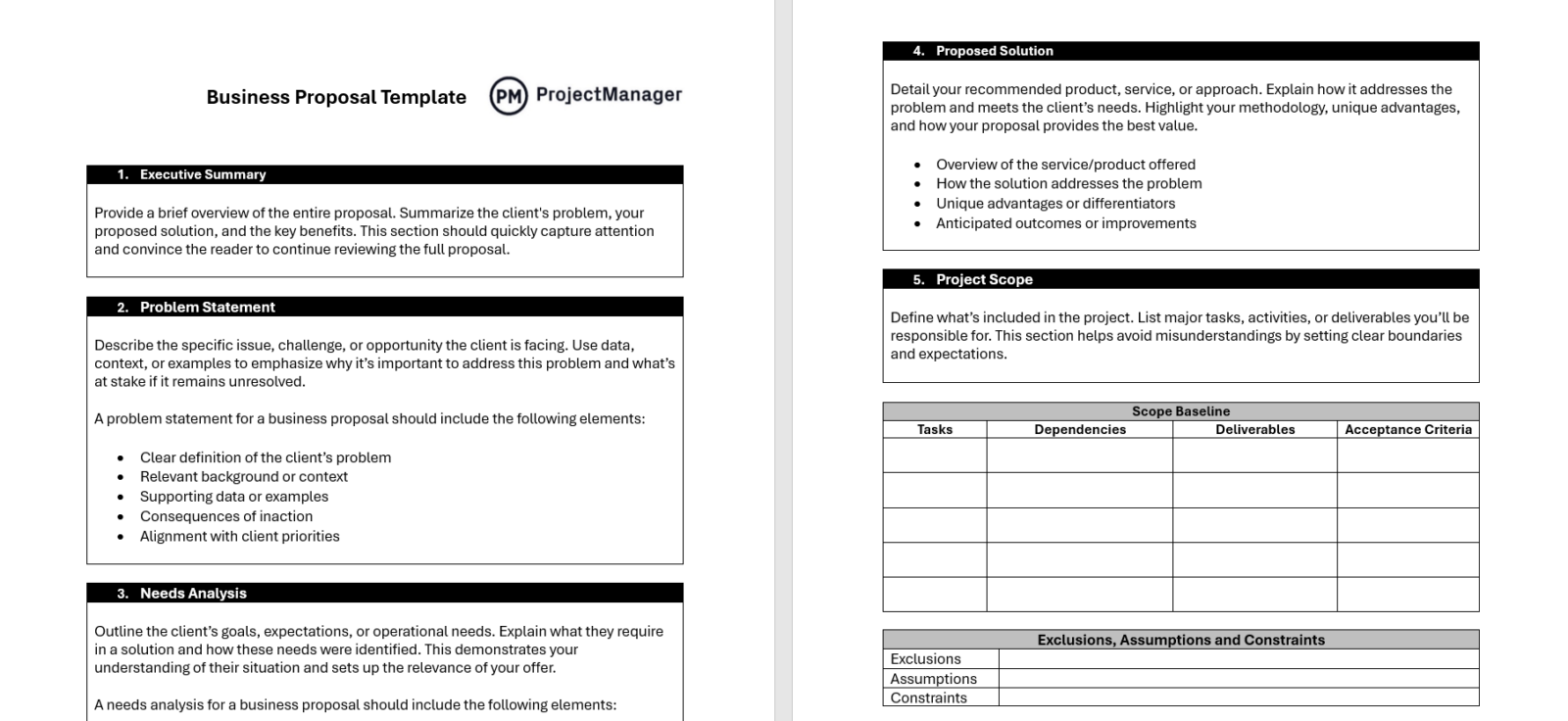
Business Proposal Template
Download this free business proposal template for outlining a company’s offerings, solutions, and value to potential clients or partners. It includes sections for problem statements, proposed solutions, pricing, timelines, and terms, helping businesses present information clearly and professionally.
Using a template saves time, ensures consistency across proposals and increases the chances of winning new opportunities.
Business Proposal Example
To better understand how a business proposal works, we’ve shared this example for a website with stagnating revenue despite steady traffic.
It shows four core needs and outlines each that will address the problem and offer a usable solution to resolve the issue.
How to Write a Work Proposal
This short guide on how to write a proposal shows a clear structure you can follow to win work. Start with a concise summary, then use defined sections to set expectations for scope, timeline and cost.
1. Project Summary
Give a brief overview of the project goals, the problem you will solve and the outcome the client can expect. Keep it focused so a reader can understand the proposal in a single pass.
2. Scope of Work
Define what is included and what is not. Specify tasks, deliverables, assumptions and any boundaries so both parties share the same expectations.
3. Project Timeline
Outline major phases, key milestones and estimated completion dates. Note dependencies and any critical path items that could change the schedule.
4. Cost Estimate
Present a clear cost breakdown by labor, materials and other expenses. Explain billing terms, payment schedule and any contingencies for out-of-scope work.
5. Terms and Conditions
Include acceptance criteria, change control liability limits and termination terms. State warranties, confidentiality and dispute resolution so obligations are clear.
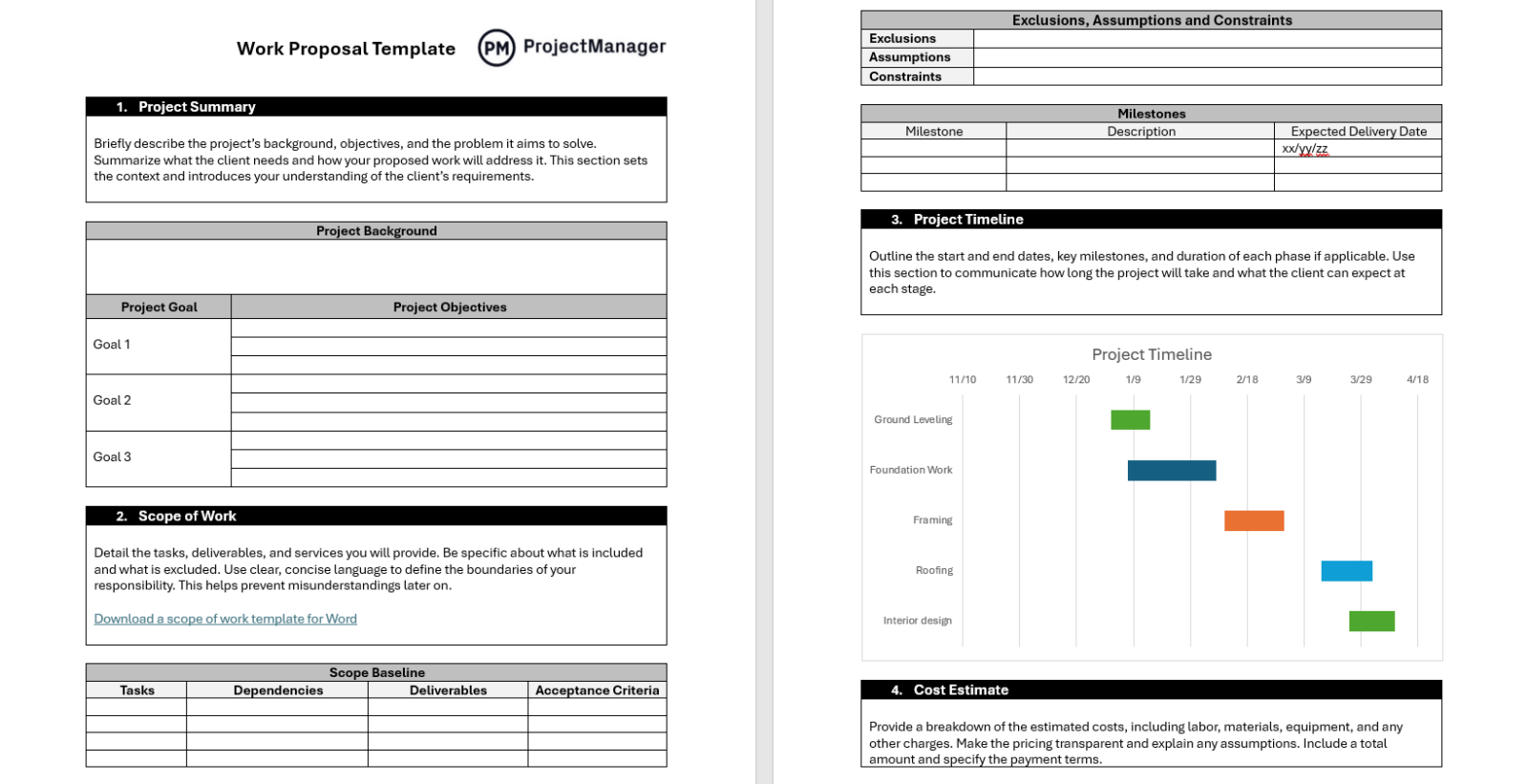
Work Proposal Template
Download this free work proposal template to outline the details of a project or service before work begins. It typically includes sections for project summary, scope of work, timeline, cost estimate and terms, giving both parties a clear understanding of expectations.
Using a template saves time, ensures consistency and makes proposals more professional and persuasive.
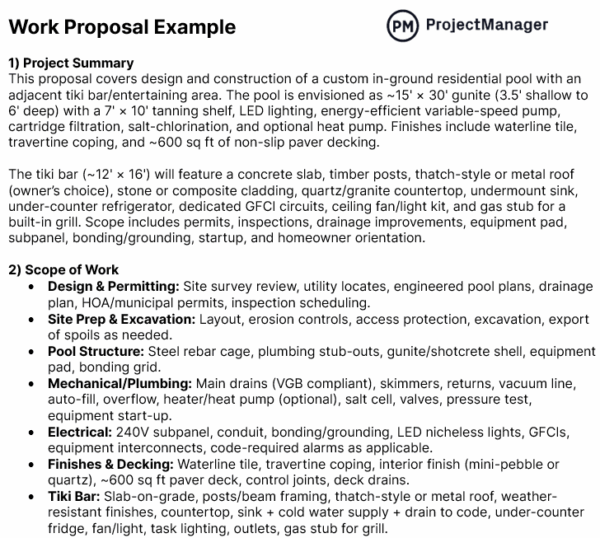
Work Proposal Example
The work proposal example will clarify how the proposal process is executed. Here, the construction proposal is for an in-ground residential pool.
The dimensions of the pool are given, including a tanning shelf, LED lighting, energy-efficient variable-speed pump, etc. As evident from the work proposal example, the scope of work is clearly defined.
How to Write a Grant Proposal
Use this guide to plan a clear grant proposal that proves need, outlines a practical solution, and shows how funds will create measurable results. Keep each section focused, evidence-based and aligned with the funder’s priorities.
1. Statement of Need
Describe the problem your community faces with data and credible sources. Explain who is affected and why current efforts are not enough.
2. Project Purpose
Summarize what your project will do and why it is the right approach. Tie the purpose directly to the documented need.
3. Goals and Objectives
Define broad goals and then set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound objectives. Make success easy to verify.
4. Project Scope
Clarify what work is included and what is not. List major activities, deliverables and key assumptions.
5. Budget Justification
Explain why each cost is necessary and reasonable. Link line items to activities and outcomes.
6. Project Budget
Provide a detailed budget with personnel, equipment and other direct costs. Note matching funds or in-kind support if applicable.
7. Project Timeline
Map phases, milestones and deadlines. Show dependencies and how you will keep work on schedule.
8. Evaluation Plan
State what you will measure, how you will collect data and who will analyze results. Include baselines and targets.
9. Sustainability Plan
Describe how the project will continue after the grant period. Include future funding, partnerships and capacity building.
10. Organizational Information
Highlight your mission, relevant experience and staff qualifications. Provide proof you can manage funds and deliver results.
Grant Proposal Template
Download this free grant proposal template to present funding requests in a clear and consistent format. It includes sections for the statement of need, project goals, budget, timeline and evaluation plan, giving funders the information they require to make informed decisions.
Using a template saves time, ensures important details are not overlooked, and increases the chances of writing a persuasive proposal.
Grant Proposal Example
This grant proposal illustrated how the United States plans to deal with a shortfall of domestically sourced lithium, critical for the development of grid-scale storage and electric vehicles.
The grand proposal example lists the project’s purpose, goals and objectives. This makes it clear what needs to be done, why and when.
How to Write an Event Proposal
Use this guide to build a clear event proposal that explains why the event matters, who it serves, and how it will succeed. Keep each section focused, evidence-based and aligned with goals the client or sponsor cares about.
1. Event Purpose
State the core reason for the event. Explain the problem or opportunity and how the event delivers value to attendees and stakeholders.
2. Event Goals and Objectives
Define broad goals, then set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound objectives. Make success easy to verify.
3. Target Audience
Describe who you want to reach by role, industry, location or interest. Explain why this audience will attend and how you will engage them.
4. Event Stakeholders
List decision makers, sponsors, partners and vendors. Clarify roles, expectations, and approvals needed at each stage.
5. Event Schedule
Outline dates, venues and major sessions. Note setup times, run of show, and critical dependencies that affect logistics.
6. Event Marketing and Promotion Activities
Explain the channels you will use, such as email, social and partnerships. Include key messages, timelines and deliverables.
7. Estimated Event Cost
Provide a high-level budget with venue, production, staffing and marketing. State assumptions and note any contingencies.
8. Event Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Select metrics that prove impact, such as registrations, attendance rate, lead volume, satisfaction and ROI. Define targets and how you will measure results.
Event Proposal Template
Download this free event proposal template to help planners present key details about an event in a clear and professional format. It covers the purpose, goals, target audience, schedule, budget and promotional activities, ensuring nothing important is missed.
Using a template saves time, keeps proposals consistent, and makes it easier to secure approval from clients or sponsors.
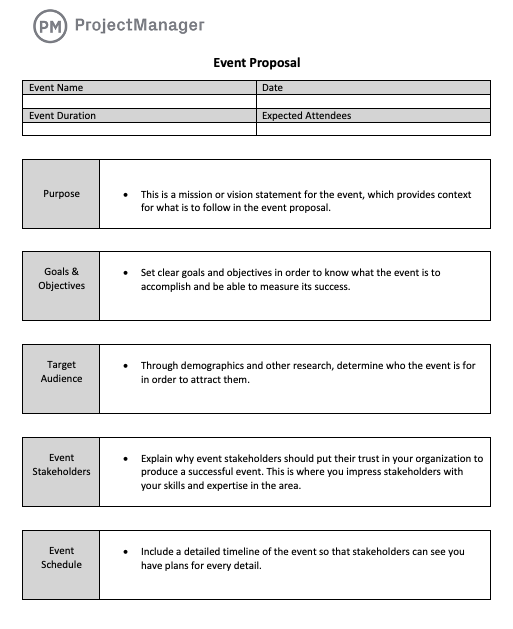
Event Proposal Example
This event proposal example is for a one-night, outdoor ticketed concert. It should be designed to showcase emerging regional artists alongside nationally recognized headliners.
The proposal shows how the purpose is to create a memorable event, generate profit and establish a repeatable model that can scale to other cities.
How to Manage Projects with ProjectManager
Once a proposal is accepted, ProjectManager makes it easy to start managing the project with multiple views that fit different work styles. Teams can plan in a Gantt chart to map tasks, dependencies and timelines, or switch to a kanban board to track workflows visually. Managers can use task lists for quick overviews and calendar views for scheduling. All views are fully connected, so updates made in one appear everywhere, giving everyone a clear and current picture of progress.
Allocate and Balance Resources
Our software includes powerful resource management tools that help managers assign tasks, track workloads, and prevent burnout. With a real-time availability chart, it’s easy to see who has capacity and who is overloaded. A color-coded workload view makes balancing assignments straightforward while ensuring deadlines stay realistic.
The software also supports a team page that provides an overview of their activity. The tool includes collaborative features that give individuals visibility into their assignments and priorities, creating a balanced and efficient distribution of work across the project.
Track Progress and Performance
There are also robust tracking features that keep managers informed at every stage. Real-time dashboards display progress on tasks, budgets and timelines without needing manual updates. Customizable reports can be generated quickly to share status with stakeholders and identify potential risks before they escalate.
Integrated time tracking ensures work hours are logged against tasks accurately, supporting better forecasting and accountability. These tracking features give project leaders the insight needed to keep projects on schedule, within budget, and aligned with objectives.
Related Content
There is more to learn about how to write a proposal. For those interested in going deeper, follow the links below to read articles that help with writing, submitting and more.
- 12 Free Proposal Templates for Submitting Proposals
- RFP Template (Request for Proposal) – Free Word Download
- How to Write a Work Proposal (with Example & Template)
- How to Write a Project Proposal (Examples & Template Included)
- How to Write a Service Proposal: Sample & Template
- How to Write a Bid Proposal (Templates Included)
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
The post How to Write a Proposal (Examples & Templates Included) appeared first on ProjectManager.