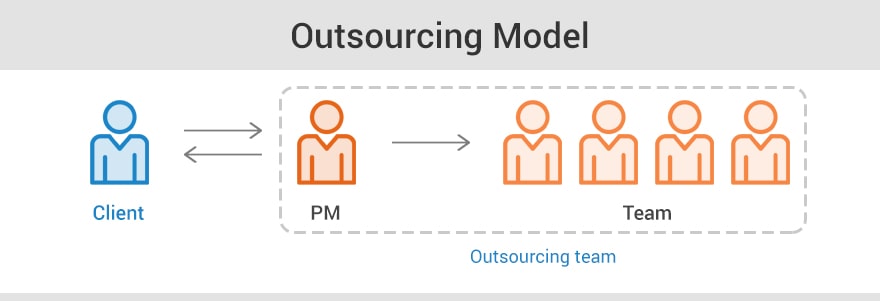
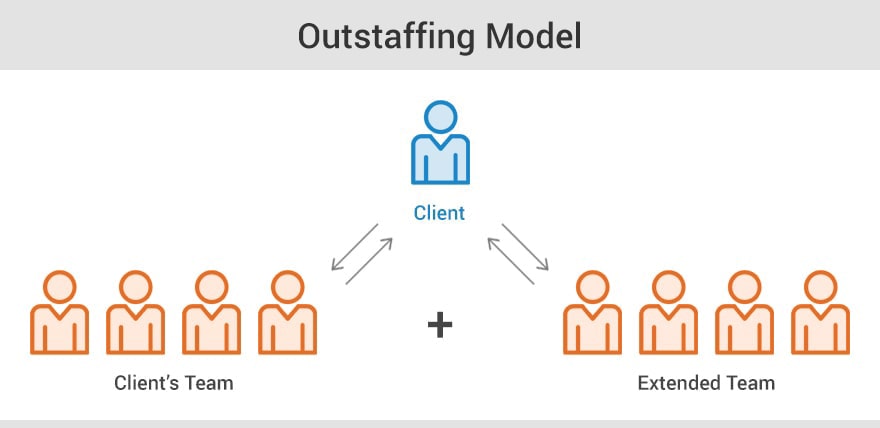
When hiring software development teams, there are several engagement models to choose from (outsourcing, outstaffing, dedicated team approach, etc).
Businesses that opt for IT outsourcing usually don’t have in-house development teams, or the team is relatively small to complete the project on time. So they need to seek and transfer the full project development and management to an outsourcing provider.
However, when a company has its own in-house development team but lacks relevant expertise or technology stack, it can add additional resources from an external provider to expand the team while staying in control of the project.
Software development outsourcing has been in the public eye for decades. According to Statista, IT outsourcing accounted for a combined revenue of $540 billion US in 2024, and during the COVID-19 lockdown, the demand for outsourcing services increased even more.
Whereas IT outstaffing is a relatively new concept. Both business models have much in common, providing significant benefits and substantial cost savings.
Nevertheless, outstaffing and outsourcing should not be mixed up, as they can be applied in different situations and pursue various business goals. Let’s check out each of these models to find out the difference between them, so you can choose the one that perfectly suits your needs.
How Software Outsourcing Works?
Hiring an outsourcing software development provider is delegating the entire project to a particular outsourcing company.
Outsourcing software development does not necessarily mean working with a company abroad; it can take place in any software development destination — either at the same location, nearshore, or offshore, depending on the size of cost savings the client wants to get.
According to the IT outsourcing model, nearly all communication and project management on the development process is handled by the Project Manager of the outsourcing organization.
The client rarely has access to the entire development team, and the team members can be involved in several projects simultaneously. In the end, the client gets a turnkey project. The final cost of the project may go beyond the allocated budget depending on the engagement model chosen.
Often, companies need more than just to complete one project, or they need ongoing development due to the size of the project. They may need to deliver large, long-term projects or a set of projects that are bound together.
In these cases, an offshore software development center (ODC) model might work better.
IT Outsourcing: What Are the Advantages?
IT outsourcing remains one of the most popular engagement models for companies that want to quickly get specialized software without managing a full in-house development team.
Manageable Project Development
Outsourcing allows companies to hand over the entire development process to a skilled service provider. From planning and design to coding, testing, and deployment, the vendor takes full responsibility for delivering a complete solution. This means businesses don’t need to manage day-to-day technical details or coordinate multiple developers.
Reduced Costs
One of the most compelling advantages of IT outsourcing is the amount of money saved in the course of achieving results.
Hiring a dedicated vendor often costs less than building a comparable in-house team, especially when factoring in recruitment, salaries, benefits, office space, and ongoing HR management.
No Management Headaches
Outsourcing eliminates much of the operational burden associated with software development. Companies don’t have to worry about onboarding developers, allocating tasks, or resolving team conflicts.
The vendor handles project management, resource allocation, and risk mitigation, which remarkably reduces stress and frees up the internal team to focus on core business activities.
Access to a Large Talent Pool
Partnering with an outsourcing company gives access to a wide pool of experts across technologies, frameworks, and industries.
Vendors often have teams of highly specialized professionals who can quickly resolve complex technical challenges.
This breadth of expertise is especially valuable when businesses need skills that are rare or difficult to recruit locally, such as blockchain development, AI integration, or advanced mobile applications.
Concentrating on Core Actions
By entrusting software development to an outsourcing partner, companies can dedicate internal resources to strategic initiatives and business growth. Instead of being consumed by technical management, they can focus on product strategy, customer engagement, and market expansion.
IT Outsourcing: Are There Any Drawbacks?
While IT outsourcing offers clear advantages, it is not without limitations. Understanding these drawbacks helps make informed decisions and put safeguards in place to avoid common pitfalls.
Less Control and Flexibility
When companies outsource a project, the vendor takes responsibility for managing the development process. While this normally reduces the workload, it also limits control over day-to-day decisions.
Adjusting priorities, making changes mid-project, or influencing the workflow can be slower and may require renegotiating contracts.
Decreased Security
Outsourcing often involves sharing sensitive information, proprietary algorithms, or customer data with a third-party team. This can raise concerns about data protection, intellectual property, and regulatory compliance.
To mitigate risks, companies need to carefully vet vendors, implement strict confidentiality agreements, and ensure they follow strong security protocols. Even so, some risk always remains when critical data leaves the company’s immediate control.
Limited Access to the Codebase
In a traditional outsourcing setup, the vendor owns the development environment and may restrict access to the full codebase.
This can make it harder to monitor progress in detail, independently troubleshoot issues, or make modifications without vendor involvement. Over time, this can create dependency on the outsourcing partner, especially if knowledge transfer is insufficient.
Expertise is Built Outside the Company
Outsourced developers work primarily for the vendor, meaning that technical expertise and institutional knowledge often remain external. While the vendor may deliver a quality product, the internal team may not fully acquire the know-how needed to independently maintain or expand the software.
Communication Problems
Geographical distance, time zone differences, and cultural variations can create communication challenges.
Misunderstandings about requirements, priorities, or project updates can lead to delays, errors, or frustration. Effective communication requires careful planning, regular check-ins, and clear documentation to ensure the team stays aligned.
Costs Can Be Higher Than Expected
Although outsourcing can reduce costs in many cases, unexpected issues such as scope changes, additional revisions, or extended timelines can increase expenses.
Fixed-price contracts may include risk buffers, which can make the initial estimate higher than anticipated. For projects with evolving requirements, outsourcing costs can sometimes surpass initial budgets, especially if frequent changes are needed.
How Does the Outstaffing Model Work?
Outstaffing is extending your team with remote employees officially working at your development company’s location. Basically, you hire a team 100% dedicated to your project and working as a part of your in-house team.
The client company will have full control over the IT team or an individual during the whole contract period. Usually, this model results in high-quality code and fast completion of the project with no extra charges.
Sketched, an outstaffing model looks like this:
In contrast to the outsourcing model, you have a choice to manage this remote team by yourself or hire remote project managers.
Outstaffing has become a strategic choice for companies that want to grow their development capacity without losing control over the product. Instead of delegating responsibility to a third party, a company strengthens its internal team with external specialists who work fully within its processes.
Outstaffing Services: What Are the Benefits?
Outstaffing services offer several tangible advantages, especially for long-term and enlarging projects.
Full Control Over the Software Development Process
One of the most important benefits of outstaffing is full operational control. Outstaffed teams work under the client’s management, follow their development standards, and participate in their sprint planning, code reviews, and daily stand-ups.
Flexibility and Scalability
Outstaffing allows companies to scale the team up or down as business needs change. They can quickly add developers with specific skills when workloads increase, or new features are planned, and reduce the team size when the demand stabilizes.
Easily Trackable Results
Since outstaffed developers are fully integrated into the client’s workflows, tracking progress and performance becomes straightforward. The company sees how specific tasks are completed, how time is allocated, and how efficiently the team delivers results.
Lower Costs Than In-House Development
Outstaffing significantly reduces the costs associated with building and maintaining an in-house team.
The client avoids expenses related to recruitment, onboarding, HR administration, office space, equipment, and employee benefits. At the same time, they pay only for the actual development resources they need.
Access to Top Talent
With outstaffing, companies are no longer limited to the local job market. They gain access to a global pool of experienced developers with specialized expertise in specific technologies, frameworks, or industries.
Faster Time-to-Market
Speed is often a critical factor in competitive markets. Outstaffing helps accelerate development by quickly assembling a skilled team without lengthy hiring processes. Developers can join the project almost immediately and start contributing after a short onboarding phase.
Outstaffing: The Drawbacks
While outstaffing offers adaptability and control, it is not a universal solution. Like any engagement model, it comes with its own challenges that you need to understand in advance.
Responsibility for Choosing and Managing Remote Developers
With outstaffing, the responsibility for team management largely remains on the client side. They are involved in selecting developers, setting tasks, monitoring performance, and ensuring that deadlines and quality standards are met.
Communication Challenges
Remote collaboration can introduce communication barriers, especially when teams are distributed across different time zones or cultural contexts.
Misunderstandings may arise if expectations, requirements, or feedback are not clearly articulated. To keep the team aligned, the company needs well-defined communication routines, documented processes, and reliable collaboration tools.
Data Security Concerns
Like with outsourcing, outstaffing often involves granting external developers access to internal systems, repositories, and sensitive business data.
This naturally raises concerns around data protection, intellectual property, and compliance. To mitigate risks, the client must establish clear security policies, sign NDAs, and work with providers that follow strong security and compliance standards.
Dependency on Third-Party Providers
Although outstaffed developers work as part of the in-house team, they are still employed by a third-party provider, which creates a level of dependency.
Changes in the provider’s business, staffing policies, or contractual terms can affect team stability. To reduce this risk, it’s important to choose a partner with long-term experience and to document knowledge and processes so they remain within your organization.
Outstaffing vs Outsourcing: What to Choose?
When it comes to the question of which model to choose for your project, the outsourcing or outstaffing one, try to answer the following questions:
- Who must be responsible for the code quality?
- Who must be responsible for project management?
- Which model is cheaper?
- Who must take part in hiring staff?
The illustration below compares the main features of each model.
When it comes to a particular business, several reasons should be taken into account when choosing this or that model.
Let’s suppose you are a startup and need to develop a software development product within a tight deadline, but you lack in-house resources.
Opting for outsourcing services here seems to be a better choice for you due to fast team ramp-up, accelerated development time, and minimal management efforts.
Companies resort to outstaffing when they lack certain specialists on their staff but do not plan to hire employees on a permanent basis.
For example, you develop your own product and have a large team in place, but due to market changes, you need to incorporate IoT, AI, or ML features; however, you do not have such experts in-house. The fastest solution will be to augment your team with experts from an outside company.
As seen, there are two options to choose from, and which one is closer to your company depends on the needs. In general, it goes as follows:
- If you already have a team of properly managed in-house IT developers, but you need extra hands for a project, then an outstaffing model will suit you best.
- If the company needs a tech solution but is not technology-focused, or it is a startup, an outsourcing model can be a good choice.
What Is the Difference Between Outsourcing and Outstaffing In Terms of Pricing?
When choosing between outsourcing and outstaffing, understanding the financial implications requires looking beyond surface-level rates.
Each model follows a different cost logic, and the total expense depends not only on developer salaries but also on project management, infrastructure, security, and technical complexity.
Outsourcing Costs
In an outsourcing model, the client typically pays a fixed price per project or per milestone, based on the vendor’s estimate of hours, resources, and expertise required.
For example, developing a mobile banking app with a frontend team, backend developers, QA engineers, and a DevOps specialist for deployment might cost $80,000–$120,000 for a 3–4 month project if outsourced to an experienced vendor in Eastern Europe.
The fixed-price model includes several layers beyond raw development:
- Project Management Overhead – The vendor provides a PM or Scrum Master to manage developers, sprints, and deliveries.
- Quality Assurance and Testing – Automated and manual testing are included to ensure the product meets standards.
- Contingency Buffers – The vendor accounts for potential delays, revisions, or unforeseen technical challenges.
Outstaffing Costs
Outstaffing costs are typically hourly or monthly per developer, giving transparency and control over resource allocation.
For example, hiring a senior React developer, a backend Python engineer, and a DevOps specialist through an outstaffing provider may cost $4,000–$6,000 per developer per month, depending on location and experience.
Unlike outsourcing, outstaffing does not include project management or fixed deliverables by default. Instead, the client integrates developers directly into their workflow, sprints, and CI/CD pipelines. This gives them the ability to:
- Adjust priorities and add features on the fly without contractual renegotiation.
- Scale the team dynamically, e.g., adding a QA engineer during testing phases or a database specialist when deploying a microservices architecture.
- Maintain ownership of code, technical architecture, and development standards.
How to Find Developers for Software Outsourcing and Outstaffing?
Finding the right developers is not just about rates or location. The success of outsourcing/outstaffing to a great extent depends on how well you define requirements, evaluate technical capabilities, and structure collaboration from the very beginning.
Step 1: Define Project Scope
You first have to understand what you want to build and why. It includes business goals, core features, expected timelines, and success criteria before contact with the vendors is made.
A detailed scope is needed for outsourcing because the pricing and timelines are tied to fixed requirements. The scope for outstaffing can be more flexible, but you still need to clearly define the roles of the developers, what seniority level is required, and responsibilities.
Overall, the clearer your scope, the easier it is to estimate effort and avoid misunderstandings later.
Step 2: Searching for IT Outstaffing Companies
Having identified the scope of work, it is time to seek outsourcing or outstaffing companies. Providers should be preferred with a high level of engineering maturity, good security practices, and low employee turnover.
Industry expertise also matters, as developers already familiar with your domain will understand typical risks, compliance requirements, and common architectural patterns.
Step 3: Review Portfolio and Client Feedback
A portfolio of a certain vendor can provide you with insight into real-world technical competencies.
Look beyond pretty pictures and focus on the architectural complexity, performance, and maintainability. Strong case studies describe challenges faced, technical decisions and tools used (or built), and measurable outcomes.
Client testimonials and reviews, in turn, will give you a proper idea about the communication quality and consistency of delivery. Long-term relationships with clients and repeat orders speak volumes about the reliability of your software development partner.
Step 4: An Interview
Especially for outstaffing, interviews are a vital step. You have to evaluate the technical depth of the developers, their ability to solve problems, and their experience with similar systems. This may include discussing past projects, reviewing code samples, or running a short technical interview or live task.
Equally important are communication skills and the ability to work within agile processes. For outsourcing, you should also interview the project manager and technical lead, as they will directly influence planning and project execution.
Step 5: Discuss Budget and Other Terms
In this stage, you align the pricing models and contractual details. For outsourcing, it typically includes fixed price or time-and-materials contracts, milestones, and over-the-scope change policies.
For outstaffing, you need to clarify hourly or monthly rates, minimum engagement terms, and developer replacement procedures.
Step 6: Hire and Onboard
Once the agreements are in place, you proceed with onboarding: giving access to repositories, development environments, and internal documentation; as well as introducing developers to your architecture, coding standards, and workflows.
Outstaffing & Outsourcing with SCAND
When you choose SCAND for outstaffing or outsourcing, you work with a development company that understands both the technical and operational sides of software development.
With over 25 years of experience in custom software engineering, we help create software products that help solve different challenges and bring tangible value.
For outstaffing, we provide dedicated developers who integrate directly into your team and workflows. You retain full control over architecture, priorities, and delivery, while we handle recruitment, HR, and administrative overhead.
You get access to carefully vetted engineers with strong expertise in .NET, cloud platforms, DevOps, AI, blockchain, and enterprise systems, allowing you to scale quickly without long hiring cycles.
For outsourcing, SCAND takes full responsibility for delivering software solutions end-to-end.
This model works well when you need a clearly scoped solution, an MVP, or a complex system delivered within defined timelines and budgets, without managing a development team internally.
In both models, we focus on engineering transparency and security. You get clear communication, direct access to specialists when needed, and well-defined processes for code ownership, data protection, and compliance.
SCAND follows proven development practices, including code reviews, automated testing, CI/CD pipelines, and secure access control, guaranteeing your software remains maintainable and scalable long term.
The Bottom Line
We have described the two options to choose from when you need to hire software developers and other IT experts. In general, if you have an in-house team but need extra hands for your current or upcoming project, then an outstaffing model will suit you best. If your company is not technology-focused or you don’t have a well-managed IT department to deliver the project within the required timeline, then outsourcing is the best option for you.
To conclude, it is important to say that each business case is unique, so when choosing between the outsourcing and outstaffing models, expert consultation would be your best choice.
At SCAND, we provide both outsourcing and outstaffing models and can help you to define which model suits you most. Feel free to contact us with any questions!
The post Outsourcing vs Outstaffing: Which One to Choose appeared first on SCAND.